Panobacumab
Monoclonal antibody designed as an antibacterial against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
 N
N Y (what is this?) (verify)
Y (what is this?) (verify) Panobacumab (proposed INN) is a monoclonal antibody designed as an antibacterial against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.[1]
It is a fully human pentameric IgM antibody with a mouse J chain.[1]
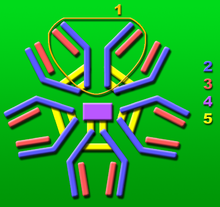
1: Base unit.
2: Heavy chains.
3: Light chains.
4: J chain.
5: Intermolecular disulfide bonds.
Development
Panobacumab is being developed by Aridis Pharmaceuticals. As of November 15th it is in phase 2 clinical trials. The originator was Berna Biotech.[2]
The mechanism of action is as a lipopolysaccharide inhibitor.[2]
References
- ^ a b International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN, prepublication copy), World Health Organization.
- ^ a b "Panobacumab - Aridis Pharmaceuticals - AdisInsight". Retrieved 15 November 2019.
- v
- t
- e
Monoclonal antibodies for infectious disease and toxins
| Human |
|
|---|
| Human |
|
|---|---|
| Chimeric | |
| Humanized |
| Human |
|
|---|---|
| Mouse | |
| Chimeric | |
| Humanized |
| Human | |
|---|---|
| Chimeric | |
| Humanized |
- #WHO-EM
- ‡Withdrawn from market
- Clinical trials:
- †Phase III
- §Never to phase III
 | This antiinfective drug article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e
 | This monoclonal antibody–related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e










